What is Reflexology?
Category Blog | Time 4 Minutes | Published November 09, 2020

 Reflexology dates back up to 6000 years ago, with evidence of the healing practice being used in Egypt and China. It is based on the principal that everything in the body is connected by nerves. The hands and bottoms of the feet contain nerve endings that connect to every organ and body system. Another principal of reflexology is vitalism, a concept which explains our bodies as being governed by an innate intelligence that monitors and promotes self-healing. The stimulation to these reflex areas during a reflexology session help stimulate the rest of the body in a way which promotes healing and balance. There are many research studies across the globe that agree that reflexology is effective at helping prevent and treat a plethora of health conditions (one of the most significant studies was published in the Journal of Multiple Sclerosis and found that “specific reflexology treatment was of benefit in alleviating motor, sensory, and urinary symptoms in MS patients.”) there is some disagreement on how reflexology works. There are four primary theories that best describe how it works:
Reflexology dates back up to 6000 years ago, with evidence of the healing practice being used in Egypt and China. It is based on the principal that everything in the body is connected by nerves. The hands and bottoms of the feet contain nerve endings that connect to every organ and body system. Another principal of reflexology is vitalism, a concept which explains our bodies as being governed by an innate intelligence that monitors and promotes self-healing. The stimulation to these reflex areas during a reflexology session help stimulate the rest of the body in a way which promotes healing and balance. There are many research studies across the globe that agree that reflexology is effective at helping prevent and treat a plethora of health conditions (one of the most significant studies was published in the Journal of Multiple Sclerosis and found that “specific reflexology treatment was of benefit in alleviating motor, sensory, and urinary symptoms in MS patients.”) there is some disagreement on how reflexology works. There are four primary theories that best describe how it works:
- Central Nervous System Adaption Theory
This theory is based on the late 19th century discovery by Englishmen Sir Henry Head and Sir Charles Sherrington that uncovered a relationship between our skin and organs, in which external stimuli (i.e., application of pressure on the hands or feed) causes the nervous system to trigger a desired healing effect.
- Gate Control Theory
The gate control theory refers to pain being an experience subjectively created by the brain, hence the pain-relieving characteristic of reflexology occurs because massage improves mood and stress.
- Vital Energy Theory
Bordering on the ancient concept of yin and yang, this theory claims that
stress impedes the flow of the “vital energy” that exists in each human body — reflexology helps keep the flow of this energy uninhibited.
- Zone Theory
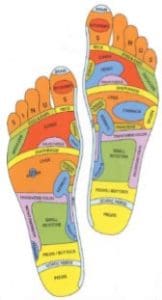
Based on the principle that our hands and feet can be charted into “reflex zones” that correspond to organs and other parts of the body.

15 Heart-Healthy Foods for Seniors to Enjoy
Blog • June 21, 2022
Healthy eating for seniors is not always top of mind, but it is especially important as we age. That’s because poor diet is a major risk factor
Read Article

Perfect Books for Seniors and Older Adults
Blog • October 25, 2022
There are countless good reasons to read. It's relaxing; it's portable. Reading is an excellent form of mental stimulation, and you can be
Read Article

Choosing the Perfect Fit in Senior Living
Blog • February 14, 2024
As your loved one ages, there will come a time when decisions must be made about the best living arrangements for them. Is remaining at home best or
Read Article
